Trauma disorders are mental health disorder that result from experiencing a severely distressing event that have a pervasive and impactful effects on an individual's everyday life. When such an event occurs, the brain instinctively shifts into survival mode, triggering a cascade of physical and emotional responses. Individuals may experience flashbacks, nightmares, anxiety, depression, uncontrollable anger, and a pervasive sense of mistrust.
These symptoms may be so severe that they hinder daily activities, impacting work, education, and personal relationships. This guide aims to delve into the various types of trauma disorders. By understanding these disorders and their treatments, we can arm ourselves with the knowledge to better manage, heal, and potentially prevent the debilitating consequences of trauma.
When someone experiences a traumatic event, their brain goes into survival mode. This can lead to a number of physical and emotional symptoms, including:
Flashbacks: Vivid memories of the traumatic event that feel like they are happening again.
Nightmares: Dreams about the traumatic event that can be disturbing and upsetting.
Anxiety: Feeling constantly on edge, worried, or afraid.
Depression: Feeling sad, hopeless, or unmotivated.
Outbursts of anger: Losing control of your temper and lashing out at others.
Difficulty trusting others: Feeling like you can't rely on anyone or that everyone is out to hurt you.
These symptoms can be so severe that they can significantly impair a person's ability to function in their daily life. They can make it difficult to work, go to school, or maintain relationships.
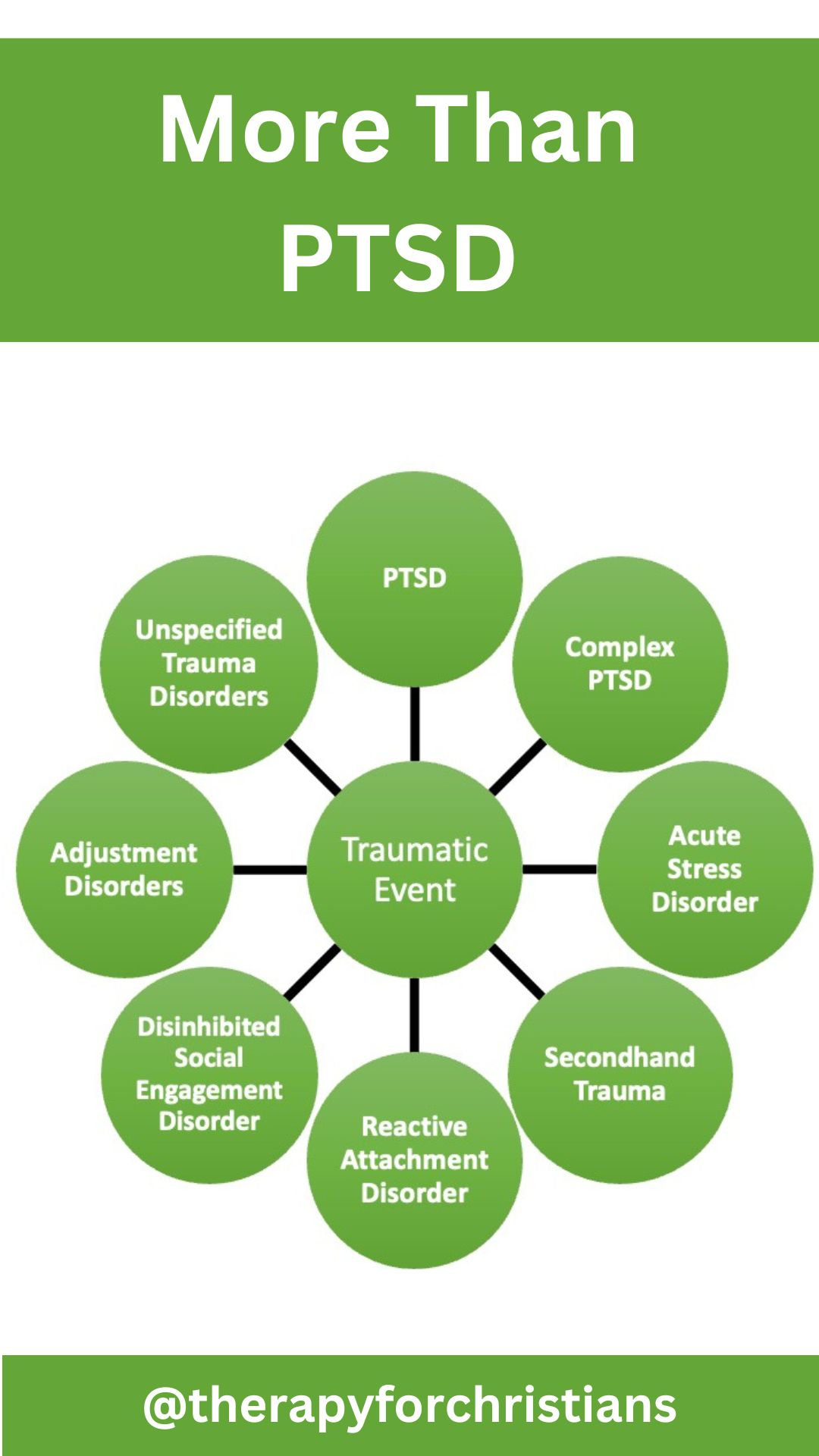
What are the seven types of trauma?
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) is a handbook used by health care professionals in the United States and much of the world as the authoritative guide to the diagnosis of mental disorders. It provides definitions, symptoms, and criteria for diagnosing mental health conditions. The DSM recognizes the below seven types of trauma disorders.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Acute Stress Disorder (ASD)
Secondhand Trauma
Reactive Attachment Disorder (RAD)
Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder (DSED)
Adjustment Disorders
Other and Unspecified Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders
However, many mental health professionals also recognize complex PTSD which is also know as developmental trauma.
1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that affects individuals who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. It can lead to intense feelings of fear, helplessness, and horror that persist long after the trauma occurred. PTSD is characterized by four main symptom clusters: intrusive memories (flashbacks and nightmares), avoidance (trying to avoid thoughts or discussions about the trauma), negative changes in thoughts and mood (negative self-image, guilt, depression, dissociation), and hyperarousal (being easily startled or having trouble sleeping).
2. Complex PTSD
Complex post-traumatic stress disorder (C-PTSD) is a mental illness that can occur after experiencing prolonged or repeated trauma. It is characterized by symptoms such as emotional dysregulation, difficulty in relationships, self-destructive behavior, and psychological vulnerabilities. People with C-PTSD often feel intense emotions like fear, shame, guilt, and despair. It can also lead to a sense of detachment or disconnection from oneself and the world.
3. Acute Stress Disorder (ASD)
Acute Stress Disorder is a short-term condition that can develop after a person experiences a severe traumatic event, typically occurring within three days to one month after the trauma. Individuals with ASD often display symptoms similar to those of PTSD, such as intrusive thoughts, negative mood, dissociative symptoms, avoidance behaviors, and arousal symptoms. However, unlike PTSD, ASD is temporary and its symptoms usually resolve within a month.
If the symptoms persist beyond this period, the individual may be diagnosed with PTSD. The primary intervention for ASD is cognitive behavioral therapy, which focuses on modifying thought patterns and behaviors that are leading to distressing symptoms. Early intervention and treatment is crucial to prevent the development of ASD into chronic conditions like PTSD. Not everyone who experiences a traumatic event will develop ASD. It largely depends on individual resilience, the severity of the trauma, and the availability of immediate emotional support.
4. Secondhand Trauma
Secondhand trauma, also known as vicarious trauma, is when we feel emotional harm because we hear about someone else's traumatic experiences. It can happen during conversations, while watching TV, or through other media. The symptoms of secondhand trauma can be similar to what witnesses experience firsthand. This includes feelings of fear, guilt, shock, sadness, helplessness, and anger.
It can also make it hard for us to connect with others and feel overwhelmed. While secondhand trauma isn't an official diagnosis, therapy can help by teaching us about it, giving us ways to regulate our emotions, and providing self-care strategies and support from family and friends.
5. Reactive Attachment Disorder (RAD)
Reactive attachment disorder is a severe and relatively rare psychiatric condition that occurs in children who have been neglected or abused in their early years. It is characterized by difficulties forming stable, trusting relationships with caregivers, peers, and adults. Individuals with RAD may display a range of behaviors such as social withdrawal, clinginess, manipulation for attention, aggression towards others, and impulsivity.
6. Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder (DSED)
Disinhibited social engagement disorder (DSED) is a rare and severe condition that can occur in children who have been neglected or abused. It is characterized by an inability to regulate behavior and emotion, especially around caregivers, peers, and adults outside the home. Individuals with DSED may display extreme impulsivity, lack inhibition when it comes to contact with strangers, and show a lack of fear when faced with potentially dangerous social situations. Treatment for DSED typically consists of individual and family therapy, parent training and skills building, medication if necessary, and behavior modification techniques.
7. Adjustment Disorders
Adjustment disorders are conditions that can develop in response to a stressful event or life change. Symptoms of adjustment disorders can include depression, anxiety, fear, worry, poor self-image, difficulty sleeping, social withdrawal, and reckless behavior. Treatment usually involves individual psychotherapy to help individuals learn healthy coping skills and strategies for dealing with their feelings.
8. Other and Unspecified Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders
Other and unspecified trauma- and stressor-related disorders are a group of conditions that may develop in response to a traumatic event or life change, but do not meet the full criteria for any other specific disorder. Symptoms can vary greatly depending on the individual's unique experience, but may include depression, anxiety, fear and worry, poor self-image, difficulty sleeping, and reckless behavior.
Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders Treatment
Treatment for trauma- and stressor-related disorders usually includes therapy, medication if necessary, and other types of support like group therapy or peer support. Cognitive behavioral therapy is commonly used to help people recognize and change negative thoughts and behaviors that cause distress. Other therapies like exposure therapy, relaxation techniques, mindfulness meditation, creative expression, and EMDR (eye movement desensitization and reprocessing) can also help manage trauma-related symptoms. Medication might be prescribed to reduce anxiety or depression.
Each person's treatment plan should be tailored to their specific needs. It's important for individuals with trauma- or stress-related disorders to find the right support and treatment to move forward in their recovery. With appropriate help, people can learn to manage symptoms and lead a more fulfilling life.
Final Thoughts on Trauma Disorders
Trauma and stress related disorders can cause significant difficulties in life, but with the right kind of help they can be managed effectively. Everyone's experience is unique, so it is important to find treatment that works for you. It is also important to remember that recovery takes time and there may be setbacks along the way. With patience, hard work, and support from family, friends, and professionals, it is possible to overcome trauma-related difficulties and lead a happier life.
One should consider seeking help from a mental health professional if they are experiencing distressing symptoms, difficulties in functioning, or any significant changes in behavior or mood. These might be signs of a mental health condition which can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment. If you need help find a Christian mental health professional, you can search our database here: database of mental health provider.
Before you leave, we would appreciate it if you helped us spread the word by sharing, tweeting, pinning, etc. this post.
About the Author:

Corine Williams, Ph.D. is Clinical Psychologist that is currently seeing clients in the States of Maryland, New Jersey, and New York. You can find out more about her practice by visiting www.therapyforchristians.com/corinewilliams. In addition to providing individual therapy, Dr. Williams is also passionate about writing books and designing merchandise that educate, uplift, and normalize mental health subject in the Christian community. You can find out more about her at www.booksbycorine.com or by visiting her amazon profile here: https://www.amazon.com/Corine-Hyman/e/B00AWZ5FL2
Help us increase mental health awareness in the Christian community by donating through our paypal link here: www.paypal.com/therapyforchristians, joining our mailing list by clicking below, or join our provider list here: Provider listing
Disclaimer: the information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this article are for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. If you are looking for a Christian counselor near you, please check out our directory located here: Christians Therapist Near Me
.png)
)-(1).jpg)